How Cybercriminals Target and Abuse Privileged Accounts Undetected

IT professionals are constantly battling cyber threats. And while the security threats may vary, many of the most hidden and undetected cyber threats these days involve privileged user accounts.
Privileged accounts are those enterprise accounts that belong to users who have been granted administrative privileges to systems. The accounts may harbor unexpected attackers, raising security concerns that serious data breaches may occur.
Because data integrity is critically important to businesses and organizations nowadays, you need to know how to protect your company’s privileged accounts from cyber threats lurking around.
It’s important to learn how to monitor privileged accounts and secure the accounts from cyber-attacks. That entails understanding the risks and methods of preventing privilege abuse.
What Is Privilege Account Abuse?
A privileged account is simply a user account that has privileges associated with it. Abuse of the accounts happens when those privileges are misused or used inappropriately without authorization.
Sometimes a privilege account abuse happens with malicious intent from attackers, while other times it happens accidentally or through willful ignorance of policies by insiders.
The 2023 Insider Threat Report by Cybersecurity Insiders states that 74% of organizations are at least moderately vulnerable to insider threats.
Meanwhile, according to a 2020 IBM Security Services report, over 90% of all security incidents involved some form of malicious privilege abuse.
Similarly, Verizon's 2017 Data Breach Investigation Report showed that privileged account abuse was the second most common cause of security threats.
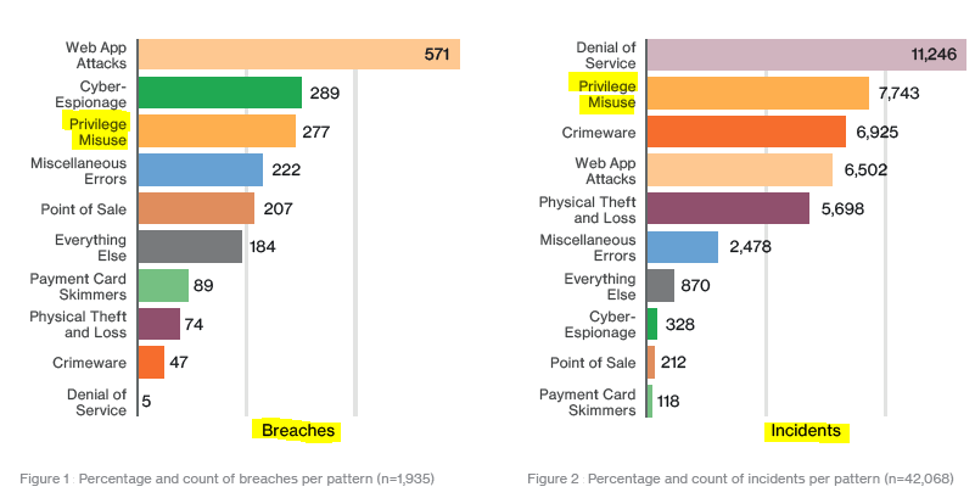
DBIR graph showing privilege misuse as one of the top causes of cyber breaches and incidents.
How Does Privilege Account Abuse Happen?
Many businesses don't monitor privileged accounts activity or limit access. And, oftentimes, privileged accounts users have more access rights than they need to do their jobs. This means access is available for use or abuse by more people.
IT management is usually in charge of user accounts, while IT security is in charge of finding threats. Privileged account abuse tiptoes on both areas and neither covers it adequately, meaning there's a lack of oversight when it comes to misused access.
Malicious actors (whether insiders or outside attackers) can exploit the lack of oversight and carry out fraudulent or malicious activity with privileged account access. Hackers can use application and operating system vulnerabilities, brute force attacks, malware, social engineering tactics, and other methods to gain privileged access.
Michael C. Redmond, Ph.D., Deputy CISO, says when attackers gain access to higher levels of system hierarchy than they are supposed to have and take control of important system components such as data and files without being detected, privileged account abuse has occurred.
Compromised privileged accounts can access sensitive data and delete, modify, or otherwise affect it, leading to severe data and security breaches. Unfortunately, privileged account abuse like those ones are common and a serious issue for organizations and businesses of all sizes.
Consequences of Poor Management of Privileged Accounts
When privileged account abuse occurs, the consequences can be dire. Access to privileges is a gateway to a system's data. So, even if a user is unintentionally misusing access, it can lead to a leak or loss of sensitive information.
Systems and applications may also shut down for periods of time, damaging business operations. This can then lead to bad publicity, loss of customer trust, and even long-term lawsuits.
Affected business might even face compliance failures and associated penalties due to privileged account abuse, and management could see steep fines or even imprisonment as a result.
Why Cybercriminals Target Privileged Accounts

Oftentimes, attackers come from outside business walls. A 2015 survey suggests that 45% of hackers prefer targeting privileged accounts because these are the accounts with a high level of access rights to sensitive data and records.
Attacking privileged accounts means hackers can access the network and make crucial changes unhindered. They can also restrict access for other users, while taking any files they want away.
Hackers know privileged accounts have more potential for criminal financial gain. Thus, they use malware, stolen credentials, and phishing schemes to gain privileged access and compromise data.
An attacker may not always restrict other users' access to their accounts in order to remain undetected. But, they can use hacked privileged accounts as a gateway into an entire system, building fake credentials and doing other fraudulent activities along the way.
Attackers may find files with people's private information, such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, phone numbers, and email addresses. They may also find bank account details, business files, and other information to sell.
Some privileged account hackers may decide to destroy key information a business needs to hurt the business undetected, while others brazenly use the data to hold the business for ransom.
Attackers don't have to be the stereotypical hooded guy in a basement. No, attackers can be anyone, including business leaders. Others are supposed entrepreneurs who turn their criminal activities into a full-blown "business," complete with salaried employees.
The Process of Attacking Privileged Accounts
A hacker can attack any kind of privileged account. This is true for both an upper management account and also someone in the mid-levels who has some privileged account access.
All that attackers usually need is one access point to get their foot in and their hands on unauthorized information. They generally follow a simple process that is effective:
- Identify and obtain any credentials that have privileged access.
- Access a separate endpoint
- Repeat and repeat until they find what they want.
How Hackers Identify Privileged Accounts
There are several steps attackers can use to identify a privileged account and target it:
- Survey the privileges of local users
- Attempt to log on with higher privileges
- Bait with a malicious file document and wait for the user to open it and infect a second endpoint.
- Use tools to walk through the endpoint's memory
- Move within the organization's user accounts
Hackers go through such steps and are determined to keep going until they break through. Sadly, it can be challenging (though not impossible) to prevent attackers succeeding if they target you.
Challenges of Preventing Privileged Account Abuse
Managing privileged account abuse threats can be difficult for organizations because it's hard to prevent hackers from accessing the controls without also preventing users from doing their jobs.
Most privileged account users have vital roles within the business or organization, hence the privileged access in the first place. They need that access to do their job. So, blocking their access can hinder their work and productivity.
Naturally, the solution would be to select individual access controls. Decide what each user can and cannot do with a privileged account. This adds a layer of security, but it may also make a highly restrictive environment that can lead to less productivity.
Controlling and Managing Privileged Account Abuse

Aside from controlling privilege abuse with role-based access control (RBAC), where user access to sensitive data or systems is limited based on their assigned roles, other effective methods of managing and reducing the risk of privileged abuse include:
i). Requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA)
MFA helps protect against account password theft by requiring additional layers of authentication beyond simply entering a username and password. This can make it more challenging for attackers and reduce the risk of cybersecurity breaches.
ii). Monitoring privileged accounts continually
By monitoring and checking audit logs and credentials such as usernames and passwords regularly, organizations can detect any suspicious activity related to privilege abuse and take appropriate action in a timely manner.
iii). Reviewing user credentials regularly
While monitoring privileged accounts also ensures you'll notice any users who are abusing privileges, regularly reviewing privileged user credentials will ensure that users have only the necessary privileges they need to perform their job.
What Happens After an Attack?
Cybersecurity management should also focus on what happens after an attack. This means your IT security team needs to watch for patterns of attacks and breaches and guard against them.
Is a privileged user showing typical unsafe or suspicious behavior? Are they accessing files they normally should not use? Are the times they're logged on suspicious in any way?
Users usually have patterns in their internet activity. It's easy to see when they log on and how they spend their time. The IT team can build a baseline profile of privileged accounts using the information in those patterns. They can then apply algorithms to watch a user's activity, identify when users deviate greatly from the pattern, and sound an alert.
If there is anything unusual happening, such as logging in at an odd time of day, security can be alerted. This can help stop cybersecurity breaches before they happen and before they go too far.
Response time is of the essence in cybersecurity, particularly when an attack happens. You shouldn’t wait for an attack to go unaddressed before responding to it. Instead, remain vigilant always and take swift action to stop attacks getting worse.
Stay alert always, secure your networks, and make it difficult for cybercriminals to target privileged accounts in your business.