Advantages of Remote Patient Monitoring - Revolutionizing Healthcare
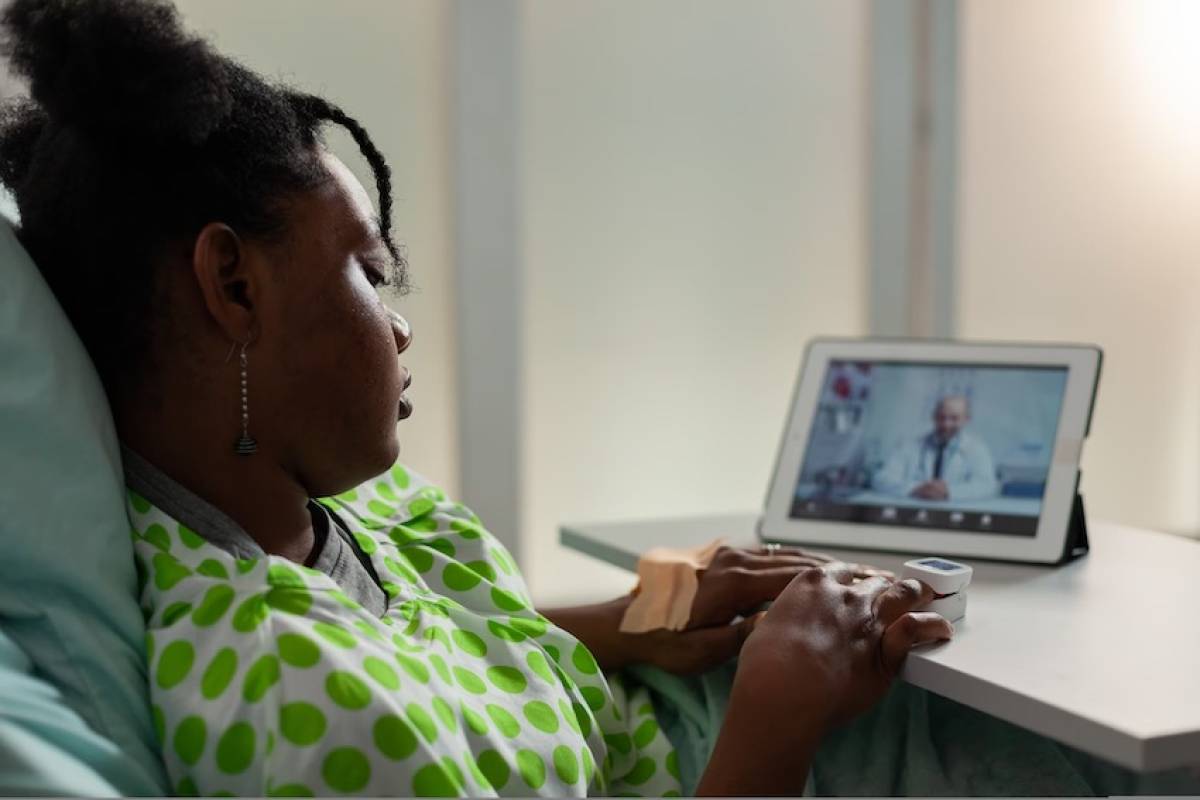

The world of healthcare is rapidly evolving, and one of the most exciting developments in recent years has been the advent of remote patient monitoring. This innovative technology allows healthcare professionals to monitor patients from afar, using a range of tools and sensors to keep track of vital signs, symptoms, and other key metrics.
From wearable devices that track heart rate and blood pressure to sophisticated software that analyzes data in real time, remote patient monitoring is revolutionizing healthcare in many ways. In this article, we'll explore some of the key advantages of this exciting technology, from improved patient outcomes to reduced healthcare costs and beyond.
So, whether you're a healthcare professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in the latest advances in medical technology, read on to learn how remote patient monitoring is changing the face of healthcare as we know it.
How Remote Patient Monitoring Works
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a method of healthcare delivery that uses technology to monitor patients outside of traditional clinical settings. RPM devices collect data on patient's health status, such as vital signs, symptoms, and medication adherence, and transmit this data to healthcare providers for review and analysis. RPM devices can take many forms, including wearable devices, mobile apps, and remote monitoring platforms.
One common example of RPM is the use of wearable devices to monitor patients' vital signs. These devices can track a range of metrics, including heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and more. The data collected by these devices is transmitted to healthcare providers in real time, allowing them to monitor patients' health status and intervene if necessary.
Another example of RPM is the use of mobile apps to track patients' symptoms and medication adherence. Patients can use these apps to record their symptoms, log their medication intake, and receive reminders to take their medication. The data collected by these apps is transmitted to healthcare providers, who can use it to monitor patients' health status and adjust their treatment plans accordingly.
Overall, RPM allows healthcare providers to monitor patients' health status more closely, identify potential health problems before they become serious, and intervene early to prevent complications.
Advantages of RPM for Patients
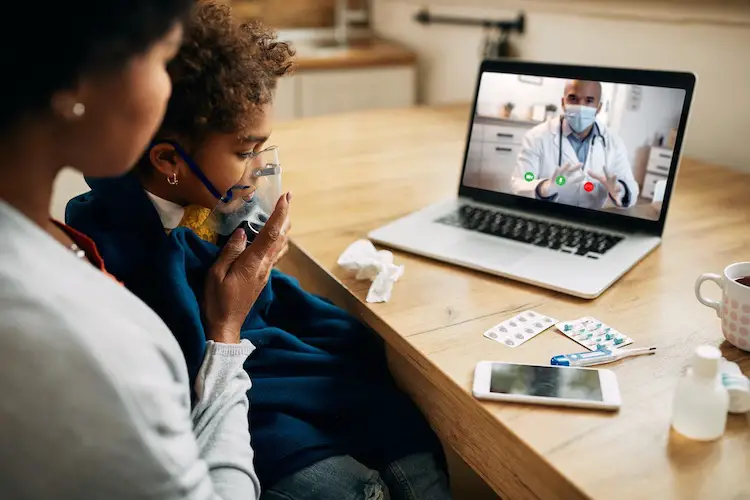

Remote patient monitoring offers numerous advantages for patients, including:
I. Improved Access to Care
One of the primary benefits of RPM is improved access to care. Patients can receive care from the comfort of their own homes, without the need for frequent visits to clinical settings. This is especially beneficial for patients with chronic conditions that require ongoing monitoring and management.
II. Increased Convenience
RPM also offers increased convenience for patients. Patients can use RPM devices and apps to monitor their health status and communicate with healthcare providers without having to leave their homes. This can reduce the time and expense associated with traditional healthcare visits.
III. Improved Quality of Life
RPM can also improve patients' quality of life by allowing them to stay connected with their healthcare providers and receive timely interventions when necessary. This can help prevent complications and reduce the need for hospitalizations.
IV. Better Outcomes
Finally, RPM has been shown to improve patient outcomes. Studies have found that RPM can reduce hospitalizations, improve medication adherence, and lead to better health outcomes overall.
Advantages of RPM for Healthcare Professionals
Remote patient monitoring also offers significant advantages for healthcare professionals, including:
I. Improved Efficiency
RPM can improve healthcare professionals' efficiency by allowing them to monitor patients' health status remotely and intervene when necessary. This can reduce the need for in-person visits and free up healthcare professionals' time for other tasks.
II. Better Patient Engagement
RPM can also improve patient engagement by allowing healthcare professionals to communicate with patients more frequently and provide timely interventions when necessary. This can help build trust and improve patients' confidence in their healthcare providers.
III. More Accurate Data
RPM devices and apps can collect more accurate data than traditional methods of monitoring patients' health status. This can help healthcare professionals make more informed treatment decisions and adjust treatment plans as needed.
IV. Improved Outcomes
Finally, RPM has been shown to improve healthcare professionals' ability to manage patients' health status and improve outcomes. Studies have found that RPM can reduce hospitalizations, improve medication adherence, and lead to better health outcomes overall.
Advantages of RPM for Healthcare Systems
In addition to the benefits for patients and healthcare professionals, remote patient monitoring can also offer significant advantages for healthcare systems, including:
I. Reduced Healthcare Costs
RPM can reduce healthcare costs by reducing the need for in-person visits and hospitalizations. This can lower healthcare systems' expenses and improve their bottom line.
II. Increased Capacity
RPM can also increase healthcare systems' capacity by allowing them to monitor patients remotely and intervene when necessary. This can reduce the need for in-person visits and free up healthcare professionals' time for other tasks.
III. Improved Coordination of Care
RPM can improve the coordination of care by allowing healthcare providers to communicate more frequently and share information more easily. This can help prevent duplicate tests and procedures and reduce the risk of errors.
IV. Better Population Health Management
Finally, RPM can improve healthcare systems' ability to manage population health by allowing them to monitor patients' health status more closely and intervene early to prevent complications. This can reduce healthcare costs and improve outcomes for entire populations.
Real-World Examples of Success Stories
Remote patient monitoring has already been shown to be effective in a variety of settings. Here are just a few examples of successful RPM programs:
I. Kaiser Permanente
Kaiser Permanente, a large healthcare system in California, has implemented an RPM program for patients with chronic conditions. The program uses wearable devices to monitor patients' vital signs and transmit this data to healthcare providers. The program has been shown to reduce hospitalizations and improve patient outcomes.
II. Veterans Health Administration
The Veterans Health Administration has implemented an RPM program for veterans with chronic conditions. The program uses mobile apps to track patients' symptoms and medication adherence. The program has been shown to improve medication adherence and reduce hospitalizations.
III. Partners HealthCare
Partners HealthCare, a healthcare system in Massachusetts, has implemented an RPM program for patients with heart failure. The program uses wearable devices to monitor patients' vital signs and transmit this data to healthcare providers. The program has been shown to reduce hospitalizations and improve patient outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Remote Patient Monitoring
Despite the many advantages of remote patient monitoring, there are also several challenges and limitations to consider. These include:
I. Cost
RPM devices and apps can be expensive, and the cost may not be covered by insurance. This can be a barrier to adoption for some patients and healthcare providers.
II. Privacy and Security
RPM devices and apps collect sensitive health data, and there are concerns about privacy and security. Healthcare providers must ensure that patient data is protected and secure.
III. Technical Issues
RPM devices and apps may encounter technical issues, such as connectivity problems or device malfunctions. Healthcare providers must be prepared to address these issues and provide alternative methods of care if necessary.
IV. Patient Compliance
Finally, patient compliance can be a challenge with RPM. Patients must be willing to use the devices and apps as directed and transmit data to healthcare providers. If patients are non-compliant, RPM may not be effective.
Future Developments in RPM Technology
Despite the challenges and limitations, remote patient monitoring is poised for continued growth and development in the coming years. Some of the key areas of focus for future RPM technology include:
I. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to revolutionize remote patient monitoring by analyzing data in real time and providing healthcare providers with insights and predictions. AI can also improve the accuracy of data collection and analysis.
II. Wearable Technology
Wearable technology is becoming increasingly sophisticated and may soon be able to monitor a wider range of health metrics. Wearables may also become smaller, more discreet, and more comfortable for patients to wear.
III. Telemedicine
Telemedicine is a related technology that allows healthcare providers to deliver care remotely. Telemedicine and RPM can be used together to provide comprehensive care to patients from afar.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
As with any healthcare technology, there are regulatory and ethical considerations to consider with remote patient monitoring. These include:
I. Data Privacy and Security
Healthcare providers must ensure that patient data is protected and secure. This includes complying with regulations such as HIPAA and ensuring that patient data is encrypted and stored securely.
II. Informed Consent
Patients must provide informed consent before participating in an RPM program. Healthcare providers must ensure that patients understand the risks and benefits of RPM and that they are willing to participate.
III. Liability
Healthcare providers may be liable for any harm caused to patients as a result of RPM. Providers must ensure that they have appropriate liability insurance and that they are following best practices for RPM.
In Conclusion
Remote patient monitoring is an exciting technology that is revolutionizing healthcare in countless ways. From improved patient outcomes to reduced healthcare costs and beyond, RPM is changing the face of healthcare as we know it.
While there are challenges and limitations to consider, the potential benefits of RPM are enormous. As RPM technology continues to evolve and develop, we can expect to see even more innovative uses of this exciting technology in the years to come.