Data Encryption: What It Is, How It Works, and Why You Should Care

Internet acces has become increasingly cheap; Social media is widespread; And information is easy to access. All this sounds great, right?
Well, they sound just as merry for those with a criminal bent of mind.
Never before in history has private information been so easy to trace and publish in the public domain. We are living in an information age, where the boon is also the curse.
Information Boon Is also the Curse
But, just like vaccinations eliminated epidemics, there is a solution to the concerns of online privacy and information security. It is called encryption.
Sounds too techie? Well, let us break encryption down into simple terms.
In the words of American computer security expert, privacy specialist and writer Bruce Schneier, there are two types encryption: “one that will prevent your sister from reading your diary, and one that will prevent your government.” In both of these cases, encryption is protecting your privacy and security.
The same case applies in the virtual environment too. Encryption creates a safety chunnel connecting the origin and destination of data, so that information that you don’t want anyone else to see is not seen.
How Encryption Works
Encryption is a modern day version of an ancient art called cryptography. Cryptography or cryptology which verbally means hidden or secret was used by the Greeks to pass sensitive war strategies and other secret information between diplomats and merchants.
The digitalized version of it is used today to encrypt information exchanged between a web user and the website, an ATM card and the bank’s server, an employee and the office network, and so on.
Today, encryption is made possible by the use of SSL certificates. An SSL certificate is a bit sized file that contains a private key and a public key which encrypts or decrypts information for safe passage.
The keys are usually of varying bit sizes. For instance, a 39-bit encryption key would have a encryption which reads like:
“EnCt210a37f599cb5b5c0db6cd47a6da0dc9b728e2f8c10a37f599cb5b5c0db6cd4
7asQK8W/ikwIb97tVolfr9/Jbq5NU42GJGFEU/N5j9UEuWPCZUyVAsZQisvMxl9h9IwEmS.”
As is evident from the example above, you cannot make any sense of the data hidden (or encrypted) within unless it is decrypted using a key. Any user who does not have the key cannot decrypt and read the message. Thus, the message can be transferred safely.
The image below shows how encryption works in a systemized environment:
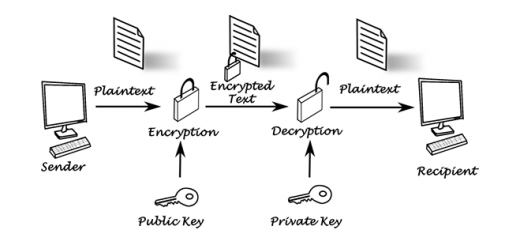
Components of Encryption
Encryption is not a single process, but a culmination of several components working together in singularity. The major components involved in encryption include:
- Information - Sensitive data that needs to be protected with encryption
- Encryption Algorithm - The program which creates the ciphertext or encrypted text of the information
- Ciphertext - The scrambled form or gibberish information produced by the encryption algorithm
- Decryption Algorithm - The algorithm which decrypts the ciphertext into unique plaintext. It basically reverses what the encryption algorithm did to create the scrambled text.
- Encryption Key - The key installed in the sender’s device. It is sent along with ciphertext to the receiver’s device.
- Decryption Key - The key which the receiver uses to decrypt to extract the information sent by the sender.
Types of Encryption
Encryption comes in different types. Some of the most common types include: Individual file and folder encryption, Volume encryption, full-disk or whole-disk encryption, Encrypted web connections, End-to-end encryptions, and so on.
- Individual file or folder encryption: As the name suggests, this type of encryption encrypts only specific type of files or folders. It is an ideal choice for businesses which has relatively fewer documents or folders to secure.
- Volume Encryption: All the files and folders contained in a volume are encrypted to a secure container.
- Full-disk or Whole-disk encryption: Encrypts and secures entire data volume contained in the disk.
- Encrypted web connections: Websites, email servers, etc. all of which need to be encrypted using HTTPS. A SSL certificate sets the stage for HTTPS encryption. It ensures that the files are locked using an encryption key and decrypted only using an authorized decryption key at the receiver’s end.
Why You Should Care about Encryption
In the digital age, anyone using the internet and other digital media like email and social media networks can have their private information breached by hackers and those looking to snoop, such as business competitors, terrorists/bad guys, or even the government.
That’s why every business, small or big, needs to encrypt its data to stay safe and secure, and to ensure customers and other stakeholders like your website visitors are safe.
Put simply, encryption is no longer an option; it's a duty you have to take seriously in order to protect the people visiting and using your website, and those passing information digitally.
Some of the ways you can use encryption to secure your confidential data include:
I) Encrypt Operating Systems
Operating systems that your device uses like Microsoft, Linux or Apple OS X can be encrypted with built-in encryption programs. Windows offers what is known as BitLocker and Apple’s FileVault, which can be used to encrypt critical files stored in your device memory.
Additionally, you can also train your staff members and system admins to secure external storage devices, USB drives or connected mobile devices to ensure data security.
II) Encrypt Your Emails
Email encryption is a must to ensure that the mails you or your business sends and receives is kept secure from any cybersecurity threat.
Further, small and medium businesses rely majorly on cloud based email servers which again need to be encrypted to ensure that hosted email data is not leaked.
Email servers can be secured using a SSL certificate or a Transport Layer Security (TLS). Similarly, Simple Mail Transfer Protocols can be used to send and receive only encrypted messages, thus creating a safe environment for all users.
Bringing it all together
Encryption is increasingly commonplace now. From encrypting parched papers that was exchanged between royals to present day digital encryption, information security has transformed in a major way. In fact, tech giants like Google, WordPress and even eCommerce websites are pushing for encryption to create a safer web environment for the global users.
For a layman, encryption can seem like a foreign concept that is difficult to understand. But, as explained in this article, encryption isn’t too hard to understand. It requires information, an encryption key, decryption key, and encryption and decryption algorithm to set up.
For businesses, the simplest form of encryption is available in the form of a SSL certificate. Using a SSL or TLS certificate you will secure your email servers, websites, operating systems and disk volumes for layered security.