Important Uses and Benefits of Ammonia in Agriculture and Manufacturing
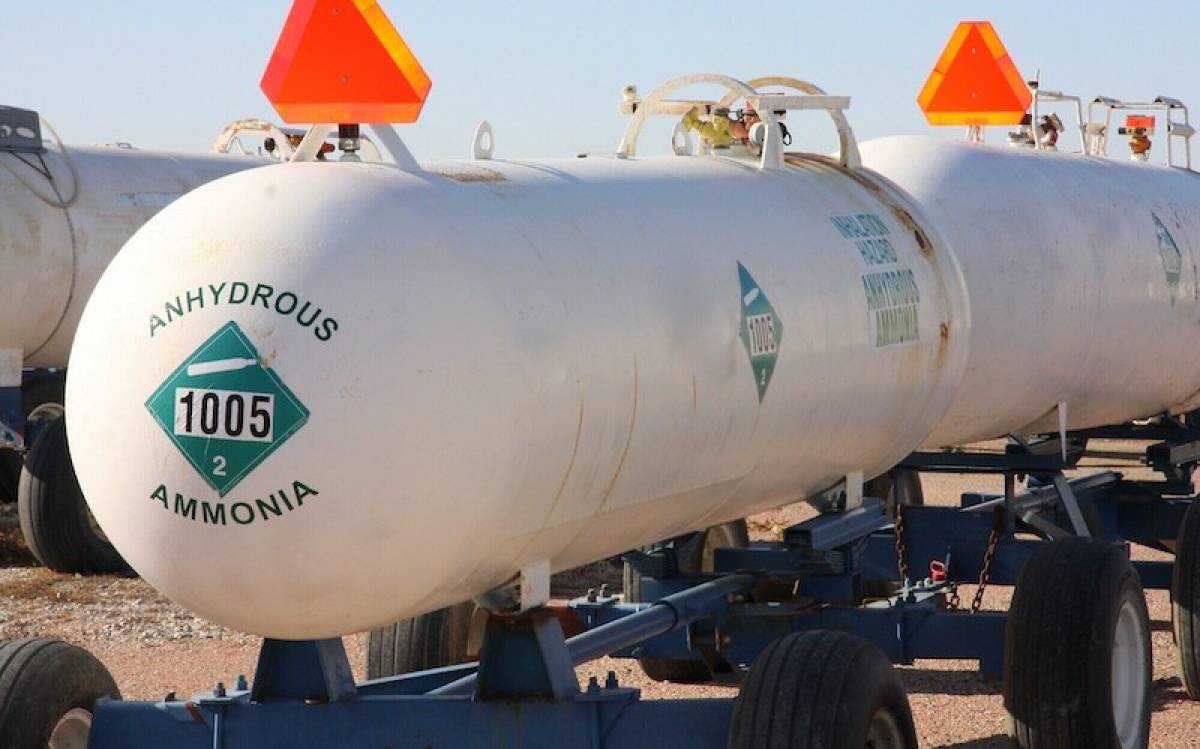

Tanks transporting ammonia to farmer's fields in western Iowa (DarcyMaulsby; iStock).
Ammonia is a chemical compound that includes nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. Also called azane, ammonia is a colorless gas that has a pungent smell. It is water-soluble with multiple applications across different industries, including agriculture and manufacturing.
In agriculture, ammonia is used as a fertilizer, a refrigerant, a fuel, and for purification of water supplies. It is also used in the manufacture of textiles, pesticides, and other chemicals. About 80% of the ammonia produced by industry is used in agriculture as fertilizer.
Ammonia occurs in the environment as part of the nitrogen cycle and is produced in soil from bacterial processes. The gas is also used in the manufacturing of anhydrous ammonia, a compound used for various cleaning applications for household and industrial use.
Since ammonia has many important uses in agriculture and manufacturing, its benefits are far-reaching – cutting across commercial, industrial, and household applications.
NH3 Benefits and Applications
Here are some of the applications and benefits of this compound in more detail:
Cleaning solution in residential and commercial areas

Ammonia is used in manufacturing ammonium hydroxide that is used as a cleaning product for households. Ammonium hydroxide (also called household ammonia) is used for windows and countertops cleaning, as well as bathroom and kitchen cleaning.
It can effectively clean toilets, tiles, tubs, sinks, and mirrors. While the undiluted chemical compound may be more effective for stains and yellowing ceramic, a dilute solution is also used around the house.
Mixing water with household ammonia can also allow for easy removal of fingerprints on glass surfaces and mirrors. It will give a sparkling finish to reflective surfaces of any kind.
A watered-down solution of ammonia is also used to clean electric ovens and stoves that have a lot of greasy residues from splatter. If any burnt remnants remain on the grill or at the base of the oven, the ammonia solution works as the perfect cleaner. It is used in commercial establishments and restaurants where tiles and stoves need to be cleaned.
Fertilizer for increased food production
The agriculture industry owes a lot to this compound, with more than 80% of ammonia used as a fertilizer. Ammonium nitrate fertilizer supplies essential plant nutrients that almost all crops require for proper growth.
For the agriculture sector to meet the needs of growing populations, use of ammonium nitrate fertilizers is very important. The fertilizers replenish the soil with lost or depleted nutrients and facilitate proper growth of the crops. This ensures increased food production.

Moreover, the ammonia compound anhydrous ammonia is also used in agriculture to prevent molding in plants and stored grains.
Refrigerant in industrial applications and manufacturing
Ammonia is used extensively in manufacturing processes across different industries. For example, in air conditioning equipment, the gas is used as a refrigerant because it has the property of absorbing heat from the surroundings and facilitating a cooler environment.
When it comes to industrial use, it is used in wastewater treatment plants. The cold storage, rubber, pulp, paper, manufacturing, and the food and beverage industries also use the gas as a neutralizer, stabilizer, and nitrogen source.
The compound is also used in a limited amount for manufacturing pharmaceutical products. It can also be used to manufacture fabrics, dyes, plastics, and explosives. It is a base product for manufacturing compounds like urea, phenol, hydrogen cyanide, amino acids, hydroxylamine, hydrazine, and ammonium carbonate.
Conclusion
So, whether it is used as a cleaning agent, a fertilizer, an acid neutralizer, or a manufacturing compound to produce several different types of plastics, ammonia has may uses in industrial, household, and commercial domains.
However, beware that ammonia is irritating and corrosive. So, exposure to ammonia can cause coughing, skin, eye, nose and throat irritation, as well as severe injury and burning of the skin, nose, eyes, throat, and respiratory tract when exposed to high concentrations of ammonia – leading to serious health issues like permanent eye damage or blindness.
Observe necessary safety precautions when handling ammonia, particularly making sure to avoid undue and high exposure to ammonia products at home.
















![Key Ways Outdoor Social Activities Make You Healthier & Happier [node:title]](/sites/default/files/styles/video_thumbnail_bottom/public/why-outdoor-social-activities-make-you-healthier.jpg?itok=axCzjZVj)
